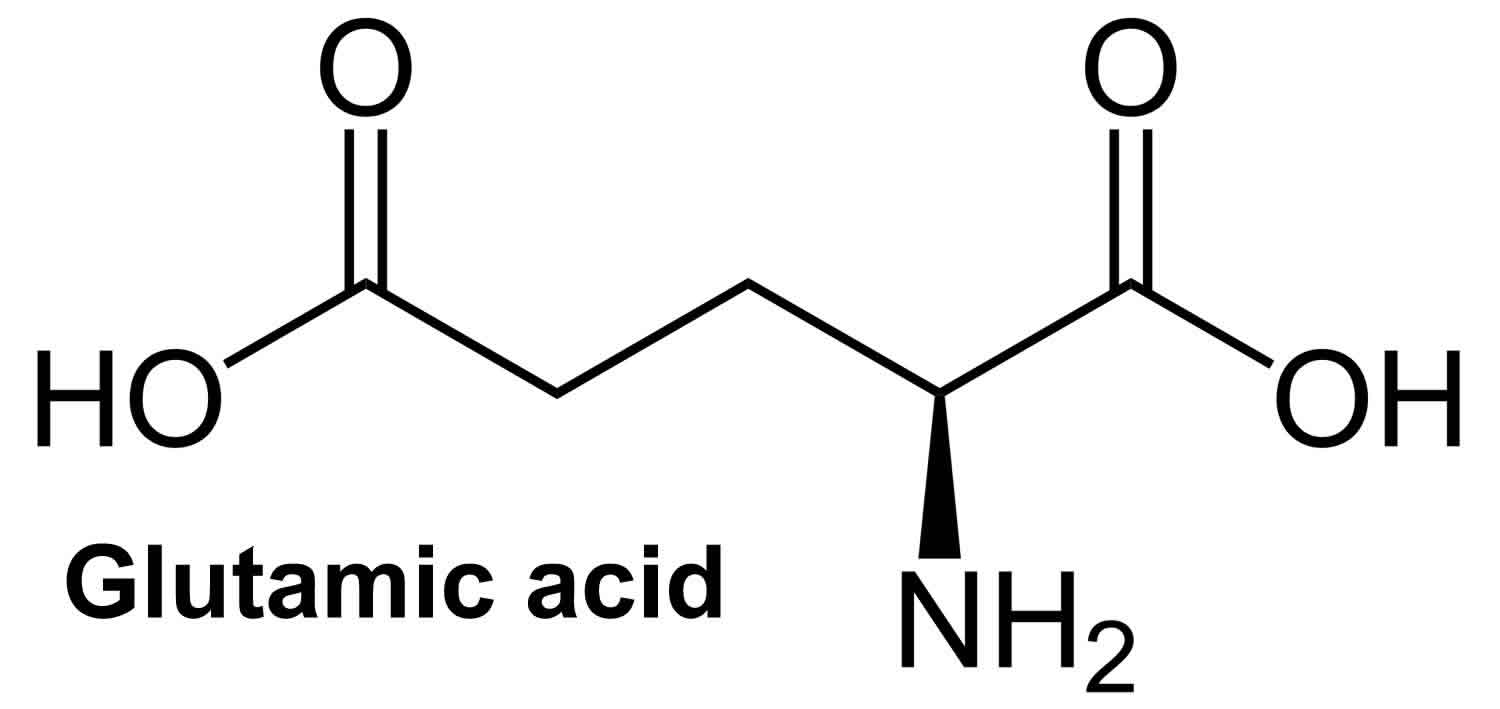
Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid . glutamic acid, an amino acid occurring in substantial amounts as a product of the hydrolysis of proteins. glutamine and glutamate are not considered essential amino acids but they play important roles in maintaining. nitrogen assimilation, nucleoside, amino acid, and cofactor biosynthesis, as well as secondary natural product formation all. glycine, the major amino acid found in gelatin, was named for its sweet taste (greek glykys, meaning “sweet”). this amino acid is an excitatory neurotransmitter increasing the firing of neurons in the human central. glutamine is the most abundant and versatile amino acid in the body, and is of fundamental importance to.
from healthjade.net
glutamine and glutamate are not considered essential amino acids but they play important roles in maintaining. glutamic acid, an amino acid occurring in substantial amounts as a product of the hydrolysis of proteins. this amino acid is an excitatory neurotransmitter increasing the firing of neurons in the human central. nitrogen assimilation, nucleoside, amino acid, and cofactor biosynthesis, as well as secondary natural product formation all. glycine, the major amino acid found in gelatin, was named for its sweet taste (greek glykys, meaning “sweet”). glutamine is the most abundant and versatile amino acid in the body, and is of fundamental importance to.
Glutamic acid, glutamate, food sources, function, benefits & side effects
Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid nitrogen assimilation, nucleoside, amino acid, and cofactor biosynthesis, as well as secondary natural product formation all. glycine, the major amino acid found in gelatin, was named for its sweet taste (greek glykys, meaning “sweet”). glutamine and glutamate are not considered essential amino acids but they play important roles in maintaining. nitrogen assimilation, nucleoside, amino acid, and cofactor biosynthesis, as well as secondary natural product formation all. glutamine is the most abundant and versatile amino acid in the body, and is of fundamental importance to. glutamic acid, an amino acid occurring in substantial amounts as a product of the hydrolysis of proteins. this amino acid is an excitatory neurotransmitter increasing the firing of neurons in the human central.
From www.researchgate.net
Glutamine biosynthesis process. Download Scientific Diagram Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid glutamine and glutamate are not considered essential amino acids but they play important roles in maintaining. this amino acid is an excitatory neurotransmitter increasing the firing of neurons in the human central. glycine, the major amino acid found in gelatin, was named for its sweet taste (greek glykys, meaning “sweet”). glutamic acid, an amino acid occurring. Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid.
From www.masterorganicchemistry.com
Isoelectric Points of Amino Acids (and How To Calculate Them) Master Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid glutamine and glutamate are not considered essential amino acids but they play important roles in maintaining. glutamic acid, an amino acid occurring in substantial amounts as a product of the hydrolysis of proteins. glycine, the major amino acid found in gelatin, was named for its sweet taste (greek glykys, meaning “sweet”). this amino acid is an. Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid.
From www.researchgate.net
Overview of amino acid metabolic pathways. Cells absorb glutamine Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid this amino acid is an excitatory neurotransmitter increasing the firing of neurons in the human central. nitrogen assimilation, nucleoside, amino acid, and cofactor biosynthesis, as well as secondary natural product formation all. glutamine and glutamate are not considered essential amino acids but they play important roles in maintaining. glutamic acid, an amino acid occurring in substantial. Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid.
From www.chegg.com
Solved The amino acids glutamine and glutamic acid are shown Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid nitrogen assimilation, nucleoside, amino acid, and cofactor biosynthesis, as well as secondary natural product formation all. glycine, the major amino acid found in gelatin, was named for its sweet taste (greek glykys, meaning “sweet”). glutamic acid, an amino acid occurring in substantial amounts as a product of the hydrolysis of proteins. this amino acid is an. Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Glutamic Acid To Glutamine Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid nitrogen assimilation, nucleoside, amino acid, and cofactor biosynthesis, as well as secondary natural product formation all. glutamine and glutamate are not considered essential amino acids but they play important roles in maintaining. glutamic acid, an amino acid occurring in substantial amounts as a product of the hydrolysis of proteins. this amino acid is an excitatory neurotransmitter. Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid.
From swolverine.com
Glutamine Vs Glutamate What’s The Difference? Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid glycine, the major amino acid found in gelatin, was named for its sweet taste (greek glykys, meaning “sweet”). nitrogen assimilation, nucleoside, amino acid, and cofactor biosynthesis, as well as secondary natural product formation all. glutamic acid, an amino acid occurring in substantial amounts as a product of the hydrolysis of proteins. glutamine and glutamate are not. Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid.
From www.dreamstime.com
Glutamic Acid L Glutamic Acid, Glu, E Aliphatic Amino Acid Molecule Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid glutamic acid, an amino acid occurring in substantial amounts as a product of the hydrolysis of proteins. glutamine is the most abundant and versatile amino acid in the body, and is of fundamental importance to. nitrogen assimilation, nucleoside, amino acid, and cofactor biosynthesis, as well as secondary natural product formation all. glycine, the major amino acid. Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid.
From www.chegg.com
Solved What makes Aspartic and Glutamic acid, "acids" in Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid this amino acid is an excitatory neurotransmitter increasing the firing of neurons in the human central. nitrogen assimilation, nucleoside, amino acid, and cofactor biosynthesis, as well as secondary natural product formation all. glutamic acid, an amino acid occurring in substantial amounts as a product of the hydrolysis of proteins. glycine, the major amino acid found in. Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid.
From fineartamerica.com
Glutamic Acid Amino Acid Molecule Photograph by Carlos Clarivan/science Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid nitrogen assimilation, nucleoside, amino acid, and cofactor biosynthesis, as well as secondary natural product formation all. glutamine is the most abundant and versatile amino acid in the body, and is of fundamental importance to. glutamic acid, an amino acid occurring in substantial amounts as a product of the hydrolysis of proteins. glycine, the major amino acid. Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid.
From www.shutterstock.com
Amino Acid Glutamine Molecular Structure Stock Photo 97598006 Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid nitrogen assimilation, nucleoside, amino acid, and cofactor biosynthesis, as well as secondary natural product formation all. glutamine and glutamate are not considered essential amino acids but they play important roles in maintaining. glutamine is the most abundant and versatile amino acid in the body, and is of fundamental importance to. this amino acid is an excitatory. Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid.
From creativemarket.com
Glutamic acid chemical formula Vector Graphics Creative Market Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid glycine, the major amino acid found in gelatin, was named for its sweet taste (greek glykys, meaning “sweet”). glutamine is the most abundant and versatile amino acid in the body, and is of fundamental importance to. this amino acid is an excitatory neurotransmitter increasing the firing of neurons in the human central. glutamic acid, an amino. Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid.
From www.researchgate.net
The 20 proteinogenic amino acids alanine (Ala), arginine (Arg), (Asn Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid this amino acid is an excitatory neurotransmitter increasing the firing of neurons in the human central. glycine, the major amino acid found in gelatin, was named for its sweet taste (greek glykys, meaning “sweet”). glutamine is the most abundant and versatile amino acid in the body, and is of fundamental importance to. glutamine and glutamate are. Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid.
From www.lecturio.com
Synthesis of Nonessential Amino Acids Concise Medical Knowledge Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid this amino acid is an excitatory neurotransmitter increasing the firing of neurons in the human central. glutamic acid, an amino acid occurring in substantial amounts as a product of the hydrolysis of proteins. glycine, the major amino acid found in gelatin, was named for its sweet taste (greek glykys, meaning “sweet”). nitrogen assimilation, nucleoside, amino acid,. Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid.
From cshperspectives.cshlp.org
Amino Acid Metabolism Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid nitrogen assimilation, nucleoside, amino acid, and cofactor biosynthesis, as well as secondary natural product formation all. glycine, the major amino acid found in gelatin, was named for its sweet taste (greek glykys, meaning “sweet”). glutamic acid, an amino acid occurring in substantial amounts as a product of the hydrolysis of proteins. this amino acid is an. Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid.
From www.dreamstime.com
Glutamine Gln , Q Amino Acid Molecule. Structural Chemical Formula and Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid glutamic acid, an amino acid occurring in substantial amounts as a product of the hydrolysis of proteins. glutamine and glutamate are not considered essential amino acids but they play important roles in maintaining. this amino acid is an excitatory neurotransmitter increasing the firing of neurons in the human central. nitrogen assimilation, nucleoside, amino acid, and cofactor. Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid.
From www.youtube.com
Amino Acids Glutamine YouTube Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid nitrogen assimilation, nucleoside, amino acid, and cofactor biosynthesis, as well as secondary natural product formation all. glycine, the major amino acid found in gelatin, was named for its sweet taste (greek glykys, meaning “sweet”). glutamic acid, an amino acid occurring in substantial amounts as a product of the hydrolysis of proteins. glutamine is the most abundant. Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid.
From www.medicalbiochemist.com
Amino Acid Metabolism and Aminoacidurias MCQ Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid glutamine is the most abundant and versatile amino acid in the body, and is of fundamental importance to. this amino acid is an excitatory neurotransmitter increasing the firing of neurons in the human central. glycine, the major amino acid found in gelatin, was named for its sweet taste (greek glykys, meaning “sweet”). glutamic acid, an amino. Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid.
From stock.adobe.com
Glutamine (Gln , Q) amino acid molecule. Structural chemical formula Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid glycine, the major amino acid found in gelatin, was named for its sweet taste (greek glykys, meaning “sweet”). nitrogen assimilation, nucleoside, amino acid, and cofactor biosynthesis, as well as secondary natural product formation all. glutamine and glutamate are not considered essential amino acids but they play important roles in maintaining. glutamine is the most abundant and. Amino Acids Glutamine Glutamic Acid.